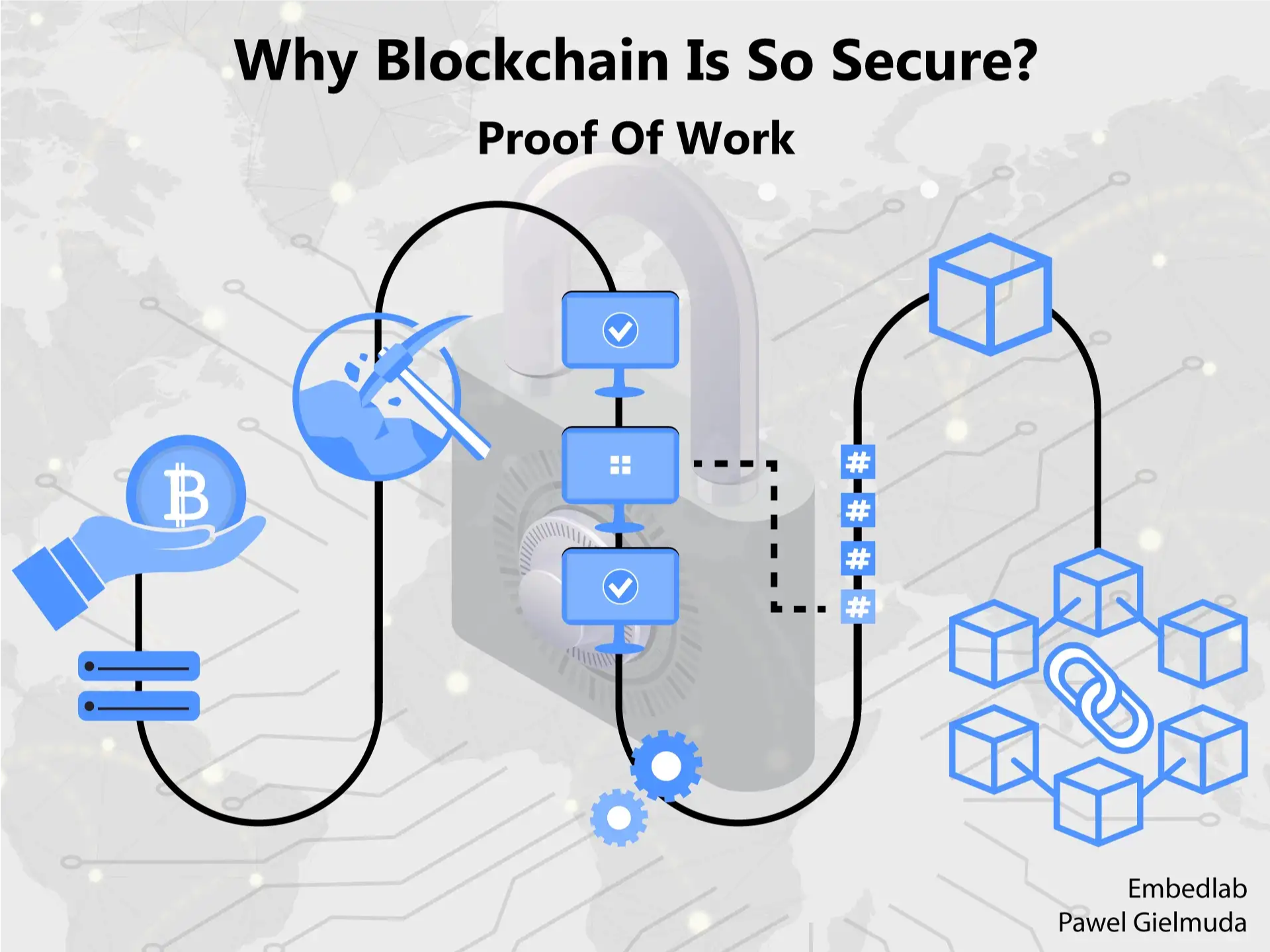
Why blockchain is secure? Previously I’ve discussed the cryptography of the Bitcoin blockchain. I mentioned that the ultimate confirmation of each block is the special hash which takes into account:
- details of transactions confirmed by digital signatures
- hash of the previous block
- rightly picked number (nonce) which gives hash special property (i.e. that it starts with 10 zeros).
The real innovation of blockchain technology is indeed the last point of the above. It enables distributed consensus about the correctness of transactions (in the case of Bitcoin’s so-called proof of work). What does this mean in detail?
Currently, when you are paying for something with a credit card, banks are the ultimate validators of the transactions. It’s their role to watch to not pay for two things with the same 10$ (so-called double spending situation). Blockchain enables the elimination of the need for external institutions. The users themselves represent this role and this is (in the case of Bitcoin) thanks to proof of work.
The concept of distributed consensus is based on the unchangeable history of transactions. If you track every payment you can be sure that there will be no double-spending. But how to make history unchangeable? One way is to make it hard to establish it in the first place. Altering it will require a similar amount of work. If you take into account that currently, the Bitcoin network consumes more than the entire country of Argentina you now get the point that this could be hard. This is the real proof of work.
In detail finding out the nonce is to pick a number that with other data will give a hash with a predefined amount of zeros at the beginning of the hash. This is by pure guessing the number and checking what would be the hash with this one. And you are not half the way if you will choose a one that will give 5 of 10 zeros at the beginning. You are still at the beginning of the process.
Miners are doing that constantly and every ~10 minutes someone guesses that and confirms a new block of transactions. If the impostor would like to alter that, he would need to be faster than others not once but every 10 minutes. In other words, he would need to take over 50% of the computational resources in the network.
As you probably understand power consumption results from its biggest strength but it could be also considered a big drawback. They are other ways of reaching a consensus in the validation of transactions but that’s a topic for a separate post.
What do think why blockchain is secure? Please share your views in comments.